Frame Rate | Everything You Need To Know
In our everyday life, whether we're watching movies, playing games, or browsing the web, the term "frame rate" always seems to catch our attention.
So, what exactly is the frame rate? It refers to the number of frames displayed per unit of time. It is a crucial metric for evaluating the smoothness of visual experiences.
Understanding frame rate is particularly important for content creators and video editors. In this article, we will delve into the concept of frame rate and explore how it influences our digital lives. Let's get started!

In this article, you will learn:
- What Is Frame Rate?
- What Is the Relationship Between Frame Rate and Persistence of Vision?
- Why Is 24 Fps the Most Common Frame Rate for Movies?
- The "Strange" Frame Rates of 59.94, 29.97, and 23.976
- What Are Frame Extraction and Frame Interpolation?
- What Are Overcranking and Undercranking?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Frame Rate
What Is Frame Rate?
The concept of frame rate is actually quite simple and can be explained in a few sentences:
In the digital age, a frame refers to a single still image. Frame rate, on the other hand, refers to the number of still images recorded or played back per second. It is measured in fps, which stands for frames per second.
In the film industry, frame rate has evolved over time. Check out this fascinating video shared by Filmmaker IQ on YouTube to learn about its interesting history.
It's worth noting that frame rate can be divided into two types: recording frame rate and playback frame rate. Usually, to achieve a realistic image that is similar to what we see in reality, it is necessary to keep the recording frame rate and playback frame rate the same.
A frame rate of 16-24 fps is already considered smooth for playback. However, since our eyes are very sensitive to subtle changes in consecutive frames, variations in brightness can be perceived, causing flickering. The greater the change in brightness, the more noticeable the flickering becomes.
Laboratory studies have shown that the human eye can distinguish up to 48 flashes per second. If the flashing frequency is increased beyond that, the changes in brightness become nearly imperceptible to the human eye.
We use Hz (hertz) as the unit to measure the number of repetitions of a periodic change per second. Artificial lights, for example, typically have a flickering frequency higher than 48 Hz. For instance, a desk lamp operating on 50 Hz alternating current (AC) flickers, but our eyes are generally unable to detect it.
This research result has also been applied to address the issue of flickering when viewing consecutive frames. Let's take movies as an example. The current standard frame rate for film projection is 24 fps.
If each frame flashes twice, there would be a total of 48 flashes per second, equivalent to a refresh rate of 48 Hz, which meets the minimum requirement to eliminate flickering.
You may often come across TVs and monitors with labels such as 60Hz, 120Hz, or 240Hz. These indicate the maximum number of frames the hardware device can display per second.
What Is the Relationship Between Frame Rate and Persistence of Vision?
When our eyes perceive an object, it forms an image on the retina, which is then transmitted to our brains through the optic nerve, creating our visual perception.
However, when the object is removed, the image doesn't immediately disappear from our vision. It persists for about 0.1 to 0.4 seconds (for moderate brightness stimuli). This characteristic of the human eye is known as "persistence of vision."
For example, if 10 frames are played continuously per second, with each frame appearing for 0.1 seconds, by the time the old image is about to fade, a new one replaces it, resulting in subtle changes between each frame.
This creates the illusion of continuous motion rather than a series of still images, and our brains perceive it as a cohesive movement.
It can be said that the principle of persistence of vision provides the scientific basis for the invention of movies, television, and animation.
Therefore, in video playback, higher frame rates theoretically result in smoother visuals, especially for fast-moving scenes. Whether recording or playing back, if the hardware allows, it's advisable to use higher frame rates.

Director Ang Lee's films "Billy Lynn's Long Halftime Walk" (2016) and "Gemini Man" (2019) were shot and screened at 60 fps and 120 fps, respectively.
Ang Lee firmly believes that 120 fps is the future. Of course, his perspective on pursuing high frame rates in movies has sparked significant controversy.
Why Is 24 Fps the Most Common Frame Rate for Movies?
Thomas Edison believed that "46 frames per second" was the minimum frame rate for movies, as anything lower would cause visual fatigue for viewers.
However, in reality, early silent films never reached this frame rate, mainly due to the cost of film and technological limitations at the time.
In 1932, "24 fps" along with "35mm film" became the internationally accepted standard in the movie industry.
When our eyes view moving objects, we perceive a kind of blur known as "motion blur." Films shot at 24 fps produce a motion blur that closely resembles how our eyes work. Additionally, 24 fps is suitable for integrating sound into movies.
Considering factors such as cost and technology, 24 fps has been the optimal frame rate to meet everyone's movie-watching needs for over a century.
However, with rapidly advancing technology, many people have started exploring higher frame rates for video recording.
Peter Jackson once explained on Facebook that movies are typically shot and projected at 24 fps not because it's the best option, but because it's the most cost-effective. However, shooting and projecting at 48 fps provides the benefit of maintaining a natural sense of speed on the screen while significantly improving the smoothness and clarity of the motion.
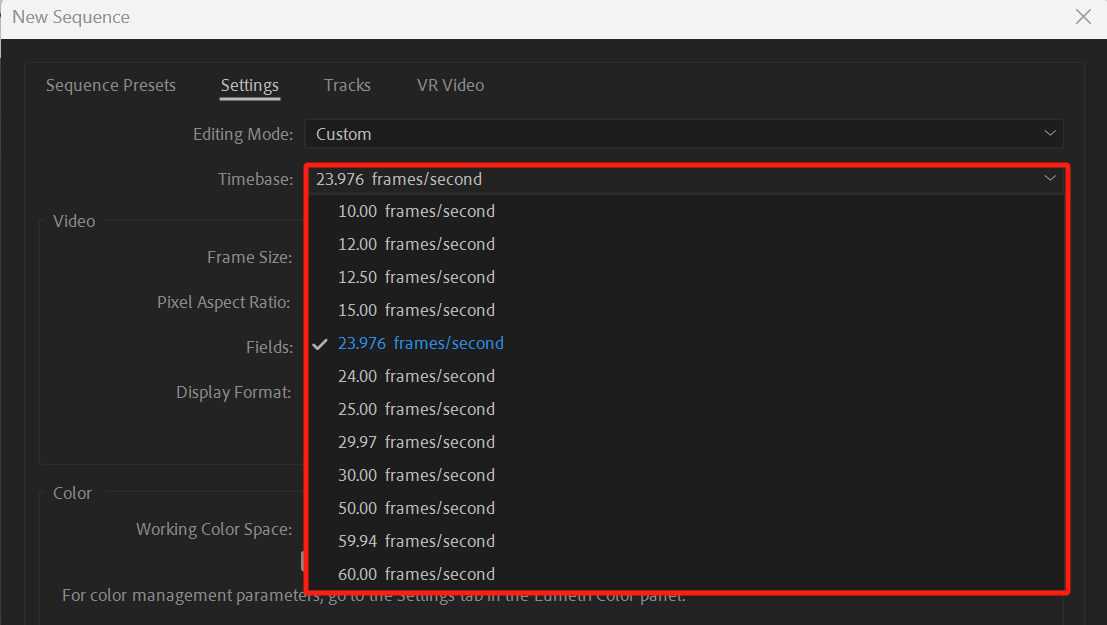
The "Strange" Frame Rates of 59.94, 29.97, and 23.976
If you've ever worked with video editing software, you may have come across frame rates like 29.97. You might wonder why it can't just be rounded to 30, considering how close the numbers are.
Well, this actually stems from the transition of the NTSC (National Television System Committee) standard from black and white to color television.
When color TV was introduced, there were compatibility issues with black and white TVs, as well as concerns about interference between color and audio signals. To address these problems, a slight reduction of 0.1% was made to the field frequency.
In other words, the field rate was decreased from 60 fields per second to 59.94 fields per second (= 60 - 60 × 0.1%). Every two fields make up one frame, resulting in 29.97 frames per second (59.94 ÷ 2).
For movies shot at 24 fps to be smoothly played on television, they also needed to be adjusted by 0.1%. This led to a frame rate of 23.976 fps (24 - 24 × 0.1%).
So, these non-integer frame rates primarily exist to meet the requirements of television standards and address certain technical issues. Video editing software offers these frame rate options to allow users to choose the most suitable one based on their needs.
With the advent of digital signals and advancements in technology, many of these parameters are no longer used and are only retained in video editing software.
What Are Frame Extraction and Frame Interpolation?
Frame extraction refers to the process of initially shooting at a higher frame rate, such as 60 fps, and then removing some frames in post-production to achieve a lower frame rate, like 25 fps.
By selectively extracting frames, the action in the footage can be accentuated, and the storage and transmission capacity can be significantly reduced. However, before frame extraction algorithms became more advanced, it could result in visual inconsistencies in the motion.
On the other hand, frame interpolation involves capturing footage at a lower frame rate, such as 25 fps, and then using software in post-production to generate additional frames for smoother playback, like 60 fps.
Obviously, the extra 35 frames per second are created by the software during post-production. Unless the algorithms are improved, there may still be noticeable differences between the interpolated frames and the actual footage.
Whether it's frame extraction or frame interpolation, the desired reference rate to convert to is often referred to as the "Timebase" in video editing software like Premiere Pro.
When it comes to video editing, improving efficiency is a challenge for content creators, editors, and digital artists.
That's where we recommend TourBox, the ultimate controller for video post-production. It simplifies every step of the video editing process, allowing you to truly focus on your creativity.

Imagine being able to manage your assets, adjust timelines, and edit clips with just one hand controlling TourBox.
Take a look at our page on how TourBox can enhance your video editing efficiency and see the significant impact it can have on your creative work.
What Are Overcranking and Undercranking?
Overcranking and undercranking are terms commonly used in video shooting:
- Overcranking refers to shooting footage at a higher frame rate, such as 240 fps, and then playing it back at a lower frame rate, like 24 fps. This creates a slow-motion effect where 1 second of footage becomes 10 seconds when played back.
- Undercranking, on the other hand, involves shooting footage at a lower frame rate, such as 18 fps, and then playing it back at a higher frame rate, like 24 fps, to achieve a fast-paced effect.
Some action films use undercranking to make the action appear more swift and intense. Time-lapse photography with a DSLR camera is a typical example of undercranking.
For example, Charlie Chaplin's "Modern Times" was shot at 18 fps. When played back at 24 fps, the actors' movements appear slightly accelerated, resulting in a comical effect.
Frequently Asked Questions About Frame Rate
Question: Why Is Frame Rate Important in Video Editing?
In video editing, frame rate determines the smoothness and clarity of the video. A higher frame rate can make the video appear more fluid, while a lower frame rate can result in a choppy playback.
Question: What Frame Rate Should Be Used for Video Editing?
It depends on your specific needs. Generally, 24 fps is the standard for movies, 30 fps for television, and 60 fps is commonly used for gaming videos.
Question: What Happens If the Frame Rate Is Changed During the Editing Process?
Changing the frame rate can affect the playback speed and smoothness of the video. For example, if you lower the frame rate, the video may appear more choppy, while increasing the frame rate can make the video appear smoother.
Question: What Is Variable Frame Rate (VFR) and Constant Frame Rate (CFR)?
Variable Frame Rate refers to a video where the frame rate can vary as needed. This can save storage space but may cause issues with audio-video synchronization.
Constant Frame Rate means the frame rate of the video remains consistent throughout, ensuring audio-video synchronization but potentially occupying more storage space.
Question: How to Adjust the Frame Rate in Video Editing Software?
Most video editing software allows you to adjust the frame rate. Typically, you can find this option in the project settings or export settings.
Product Recommendation:
If you haven't experienced TourBox yet, take a look at our latest product, TourBox Lite. TourBox Lite offers great value for money and is perfect for first-time users of TourBox.

That concludes our article on frame rate. Thank you for watching. We are sure you now have a better understanding of what frame rate is and won't feel lost when editing videos.